Essential Guide to Backup Power Generators
Introduction to Backup Power Generators
In today’s fast-paced world, a reliable power supply is essential for both homes and businesses. Power outages, whether due to natural disasters or grid failures, can lead to significant disruptions. Backup power generators serve as a critical solution, providing an alternate source of electricity when the main power supply fails. This guide explores the various aspects of backup power generators, helping you understand their importance, types, and how to choose the right one for your needs.
Understanding the Types of Backup Power Generators
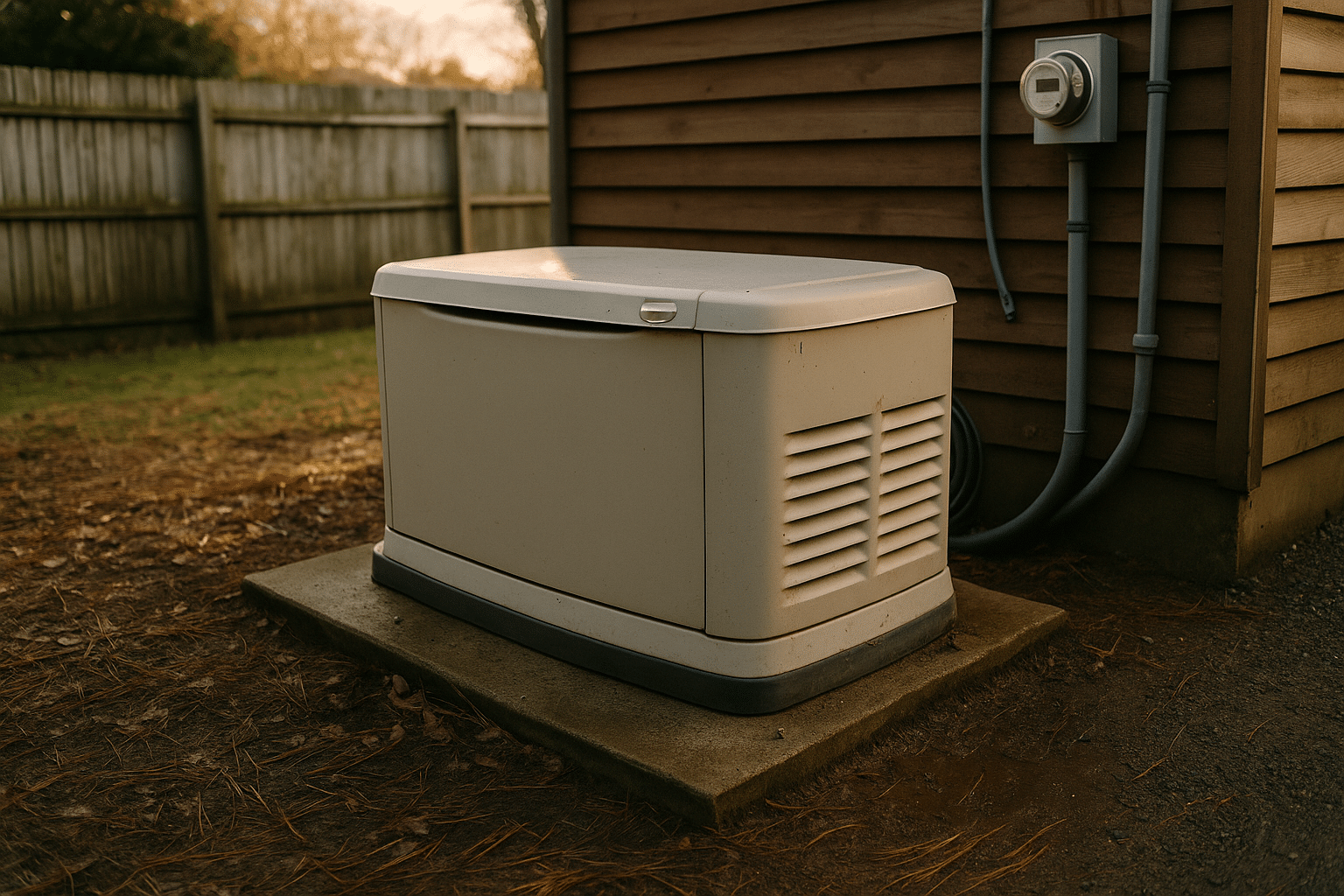
Backup power generators come in various types, each designed to meet specific needs. The most common types include portable generators, standby generators, and inverter generators. Portable generators are versatile and can be moved to different locations, making them suitable for temporary setups or outdoor events. Standby generators are permanently installed and automatically activate during a power outage, providing seamless power supply to critical systems. Inverter generators, on the other hand, are known for their quiet operation and fuel efficiency, making them ideal for sensitive electronics.
When selecting a generator, consider factors such as power output, fuel type, and noise level. Portable generators typically run on gasoline, while standby generators often use propane or natural gas. Inverter generators are popular for their ability to adjust engine speed based on the electrical demand, enhancing fuel efficiency and reducing noise.
Key Features to Consider
When choosing a backup power generator, several key features should be taken into account to ensure it meets your specific requirements. Power output is one of the most critical factors. Calculate the total wattage of the appliances and systems you need to power during an outage. This will help you determine the generator’s capacity. Additionally, consider the fuel type and availability in your area. Propane and natural gas are often preferred for their cleaner emissions and longer shelf life compared to gasoline.
Another important feature is the generator’s runtime. This indicates how long the generator can operate on a full tank of fuel. For long-term outages, a generator with a longer runtime is beneficial. Noise level is also a consideration, especially if you live in a residential area. Inverter generators are generally quieter and may be a better option for noise-sensitive environments.
Installation and Maintenance Tips
Proper installation and maintenance are crucial for the optimal performance of backup power generators. Standby generators require professional installation to ensure they are connected to your home’s electrical system correctly. This includes setting up an automatic transfer switch that detects power outages and switches the power source from the grid to the generator seamlessly.
Regular maintenance is essential to keep the generator in good working condition. This includes checking fuel levels, oil changes, and inspecting the battery. It’s also important to run the generator periodically to ensure it starts and runs smoothly. Many manufacturers recommend running the generator for a few minutes every month to prevent engine issues.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Generator for Your Needs
Choosing the right backup power generator involves evaluating your specific power needs, understanding the types of generators available, and considering key features such as power output, fuel type, and noise level. By taking the time to assess these factors, you can select a generator that provides reliable power during outages, ensuring the safety and comfort of your home or business.
Remember, proper installation and regular maintenance are critical to the longevity and efficiency of your generator. With the right backup power solution, you can have peace of mind knowing you’re prepared for any unexpected power disruptions.